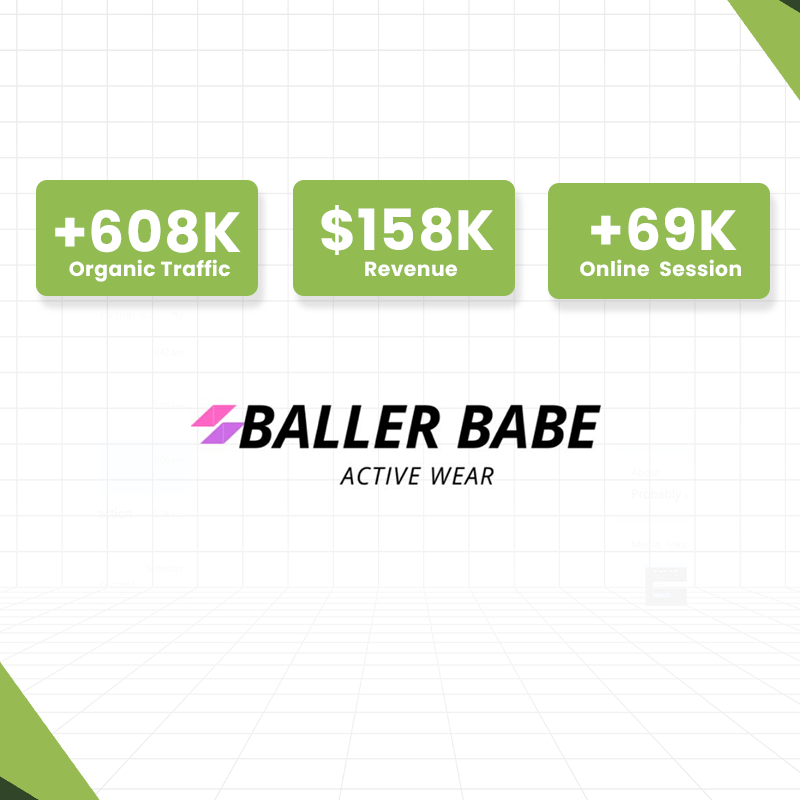
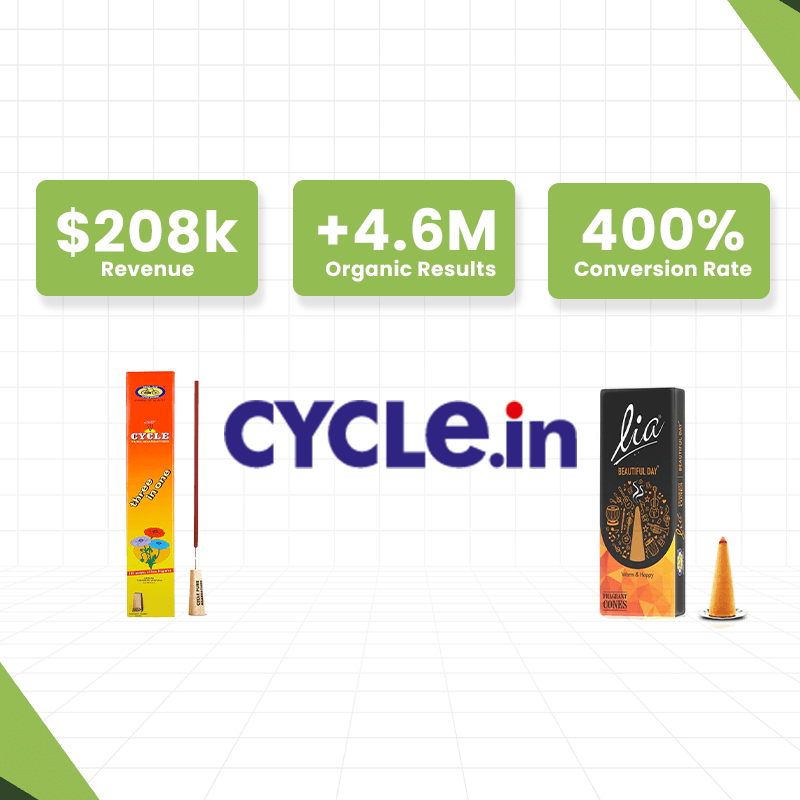
Ecommerce has grown into a global powerhouse, with retail ecommerce sales surpassing $5.7 trillion in 2022 and expected to reach new peaks in the coming years. Let's break it down.
What is ecommerce?
Ecommerce, or online shopping, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services via digital platforms. This wide-reaching concept covers everything from retail sites and marketplaces to banking and even online auctions.
How did ecommerce start?
The seeds of ecommerce were sown in the 1960s with the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), which helped transfer documents between supply chains. The first known online transaction was less traditional—a marijuana sale between students at Stanford and MIT via ARPANET in the early '70s. By 1994, the first formal ecommerce sale was made on NetMarket, marking the beginning of modern online retail.
Types of ecommerce business models

B2C (Business to Consumer):
The most familiar model. When you shop on Amazon, Wayfair, or Etsy, you're engaging in B2C.
B2B (Business to Business):
Often overlooked, B2B ecommerce is booming. Alibaba and Salesforce are key examples.
C2C (Consumer to Consumer):
Think of peer-to-peer platforms like Poshmark and thredUp, where users sell second-hand items.
C2B (Consumer to Business):
Individuals sell products or services to companies, such as freelancers offering skills on Fiverr.
D2C (Direct to Consumer):
Businesses sell directly to customers, bypassing middlemen. Shopify projects D2C sales will hit $161.22 billion by 2024.
B2A (Business to Administration):
Online services for government agencies, such as IBM providing cloud computing to public institutions.
C2A (Consumer to Administration):
Citizens engaging in transactions with government bodies, like online tax filings.
Key components of an ecommerce website
Ecommerce sites vary widely, but certain elements are essential:

- Online catalog: A well-organized collection of products, with appealing visuals and descriptions.
- Shopping cart: A virtual basket where users can store potential purchases before checkout.
- Payment gateway: A secure system for processing transactions, like PayPal.
- Order management system (OMS): Tracks orders, inventory, and customer queries to streamline fulfillment.
Advantages of ecommerce
- Convenience: Shoppers can access products from anywhere, at any time.
- Broader selection: Online stores offer far more variety than physical ones.
- Lower costs: Without physical locations, businesses save on overhead.
- Global reach: Products can be sold worldwide, as long as logistics are handled efficiently.
- Personalized shopping experiences: Data-driven recommendations boost sales and enhance customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages of ecommerce
- Lack of personal interaction: Online shopping can feel impersonal, lacking the tactile experience of brick-and-mortar stores.
- Shipping costs and wait times: These can deter buyers, especially when instant gratification is expected.
- Security concerns: Sharing financial information online makes some wary of data breaches.
- Returns and refunds: Returning items can be a hassle, especially for international transactions.
- Intense competition: The global nature of ecommerce means sellers face stiff competition 24/7.
Where is ecommerce headed?
Several trends are shaping the future of ecommerce:
- Augmented and virtual reality: These technologies are revolutionizing how customers experience products online, from trying on clothes to visualizing furniture in their homes.
- Subscription-based models: D2C businesses are increasingly offering subscription services, like Barkbox and Dollar Shave Club, to enhance convenience and personalization.
- Sustainability: As consumers become more eco-conscious, businesses are shifting towards ethical practices and sustainable sourcing, reflecting a growing demand for responsible consumerism.
The ecommerce landscape is ever-evolving, and with innovations like AI and AR on the rise, the future promises even more personalized and seamless shopping experiences.